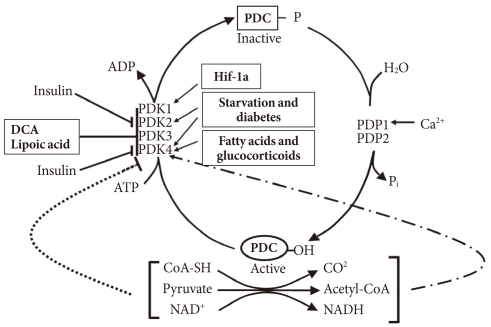
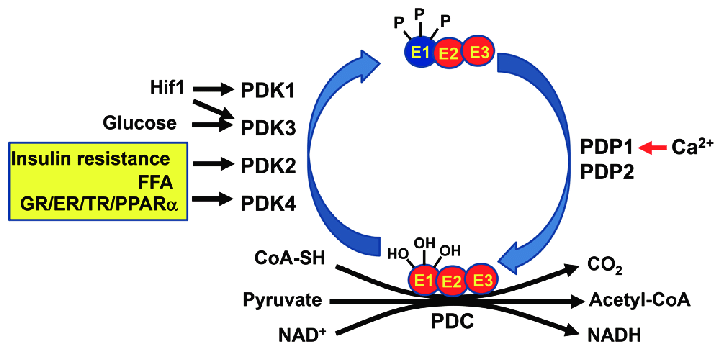
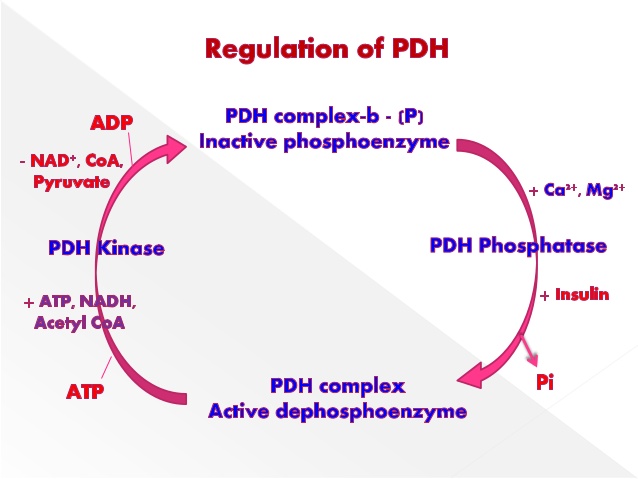
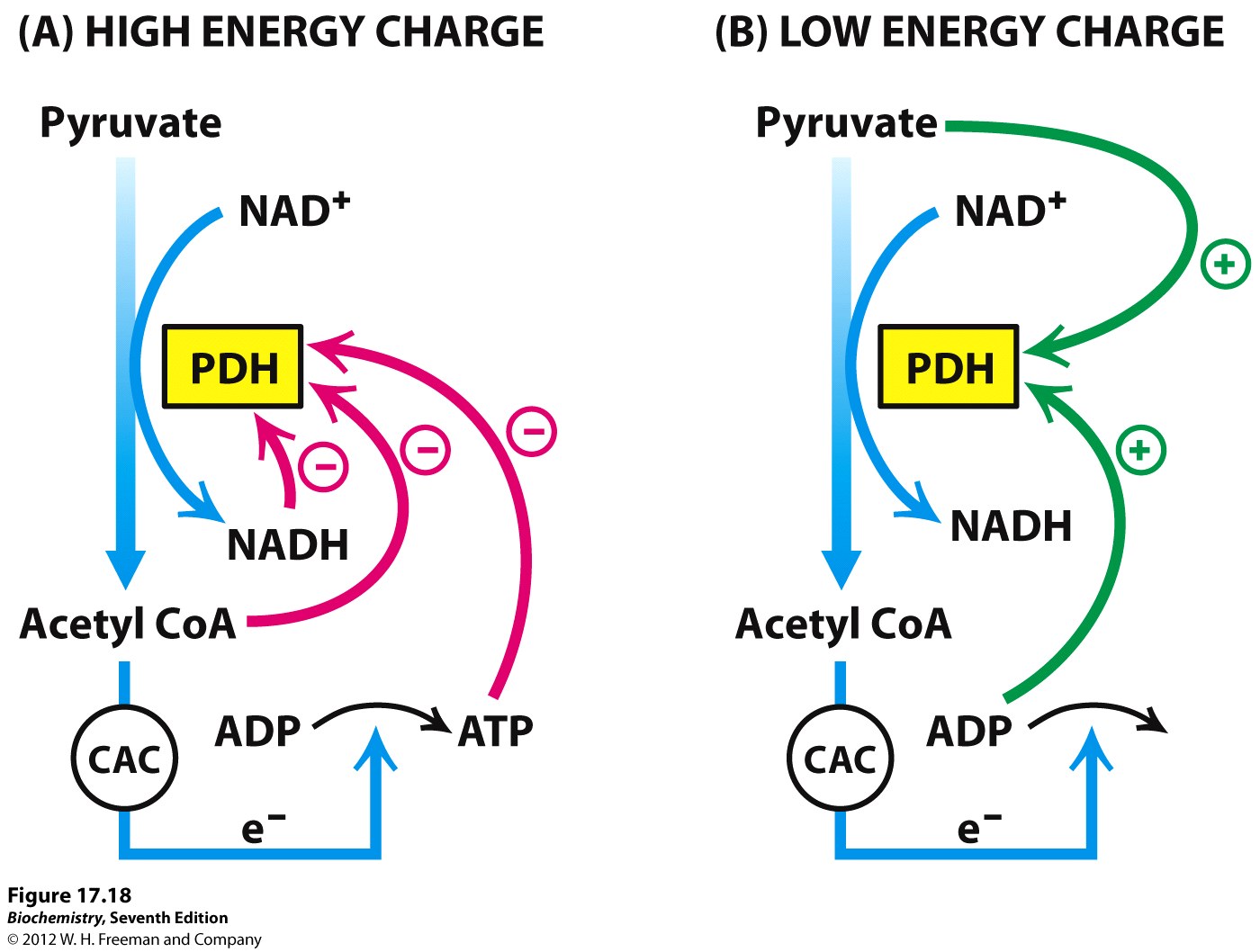
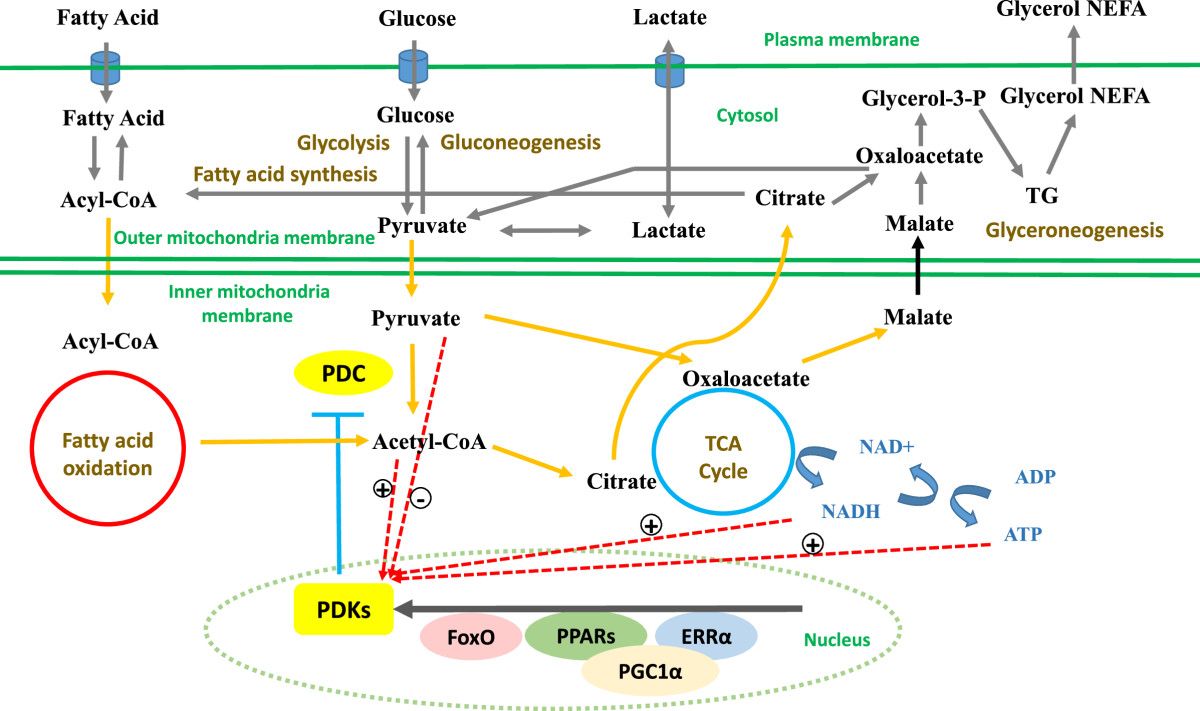
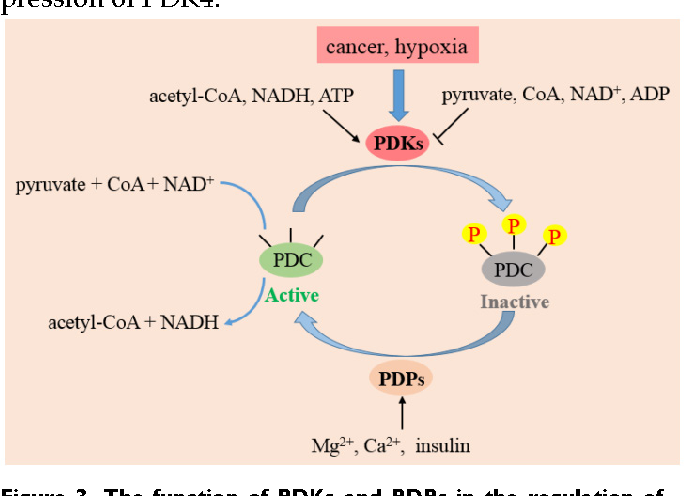
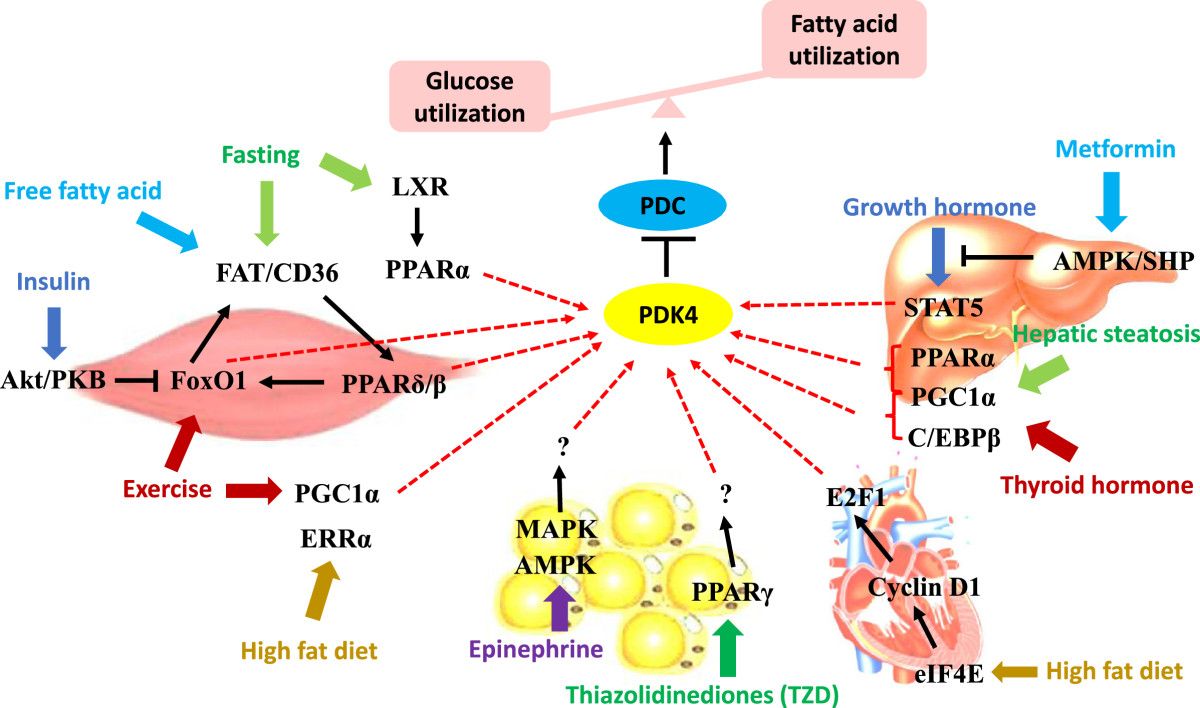
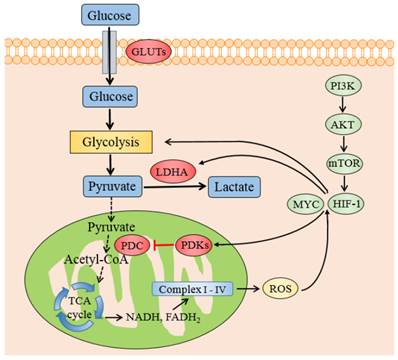
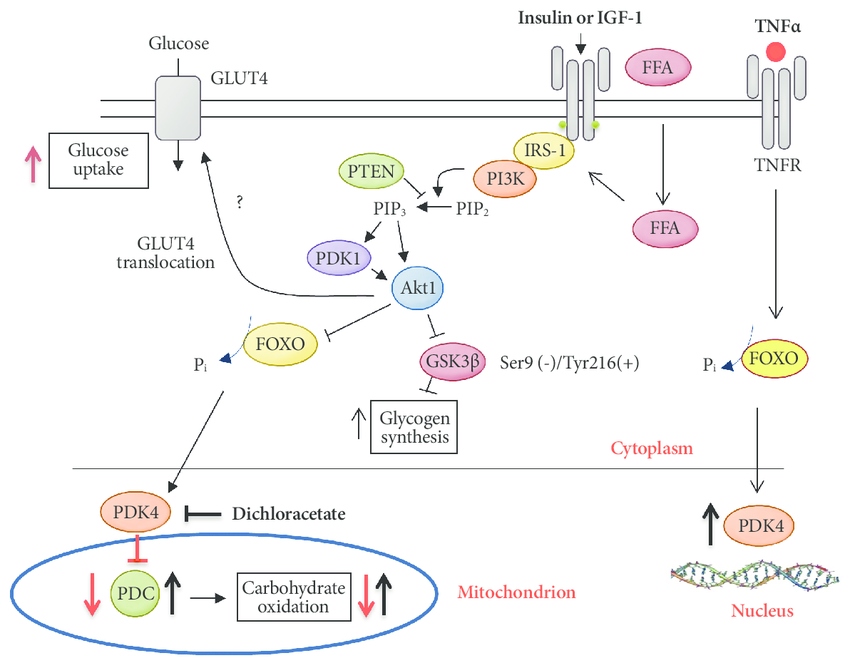
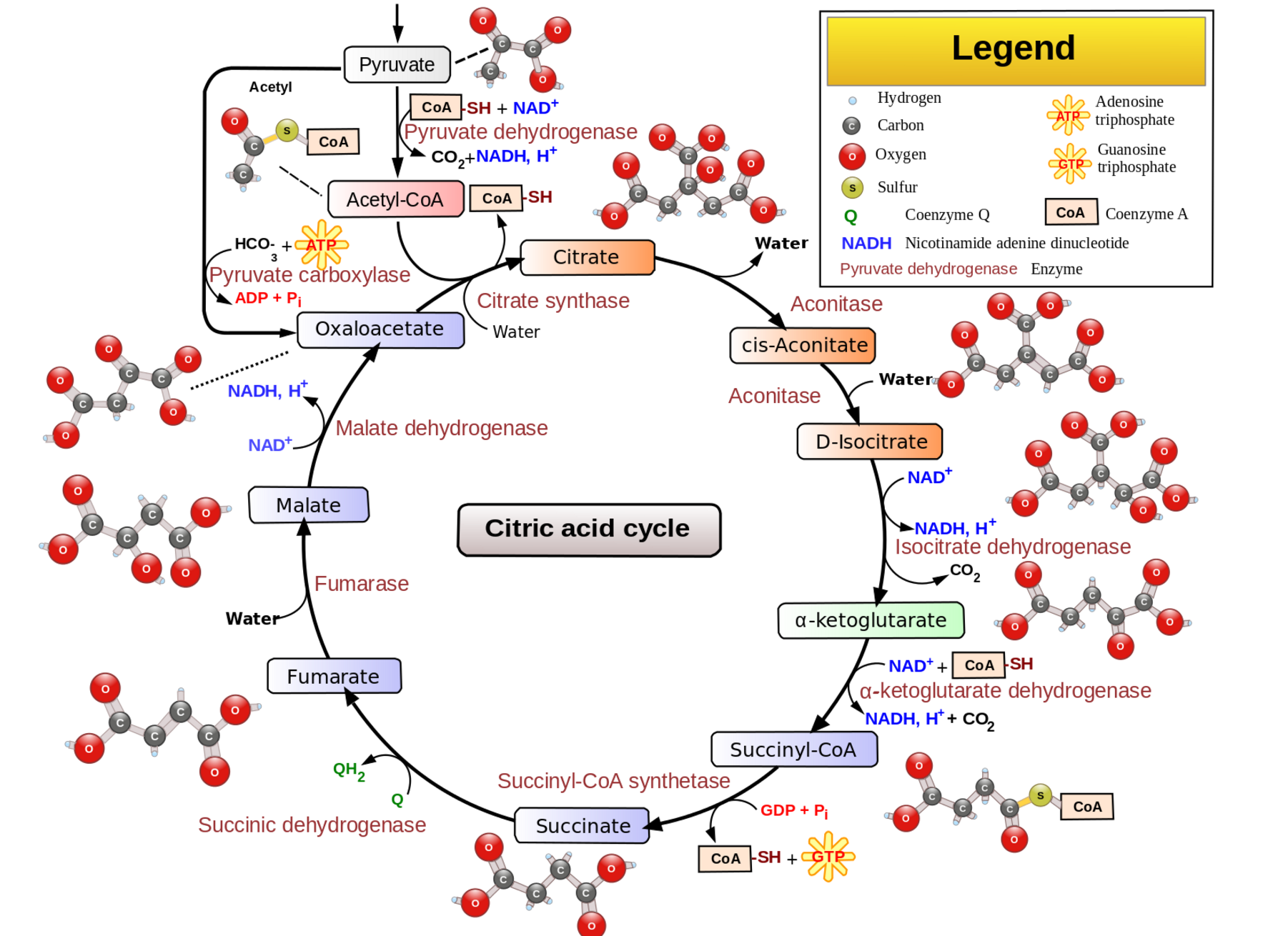
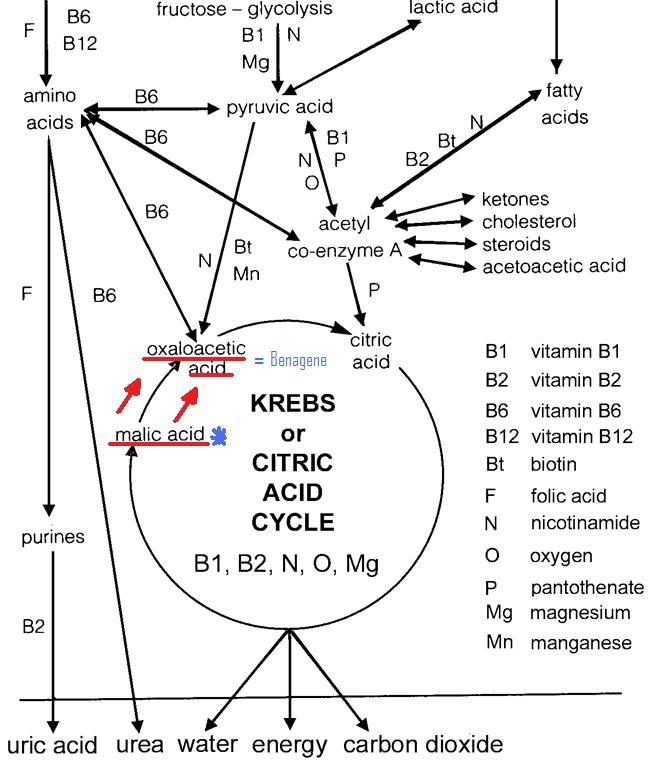
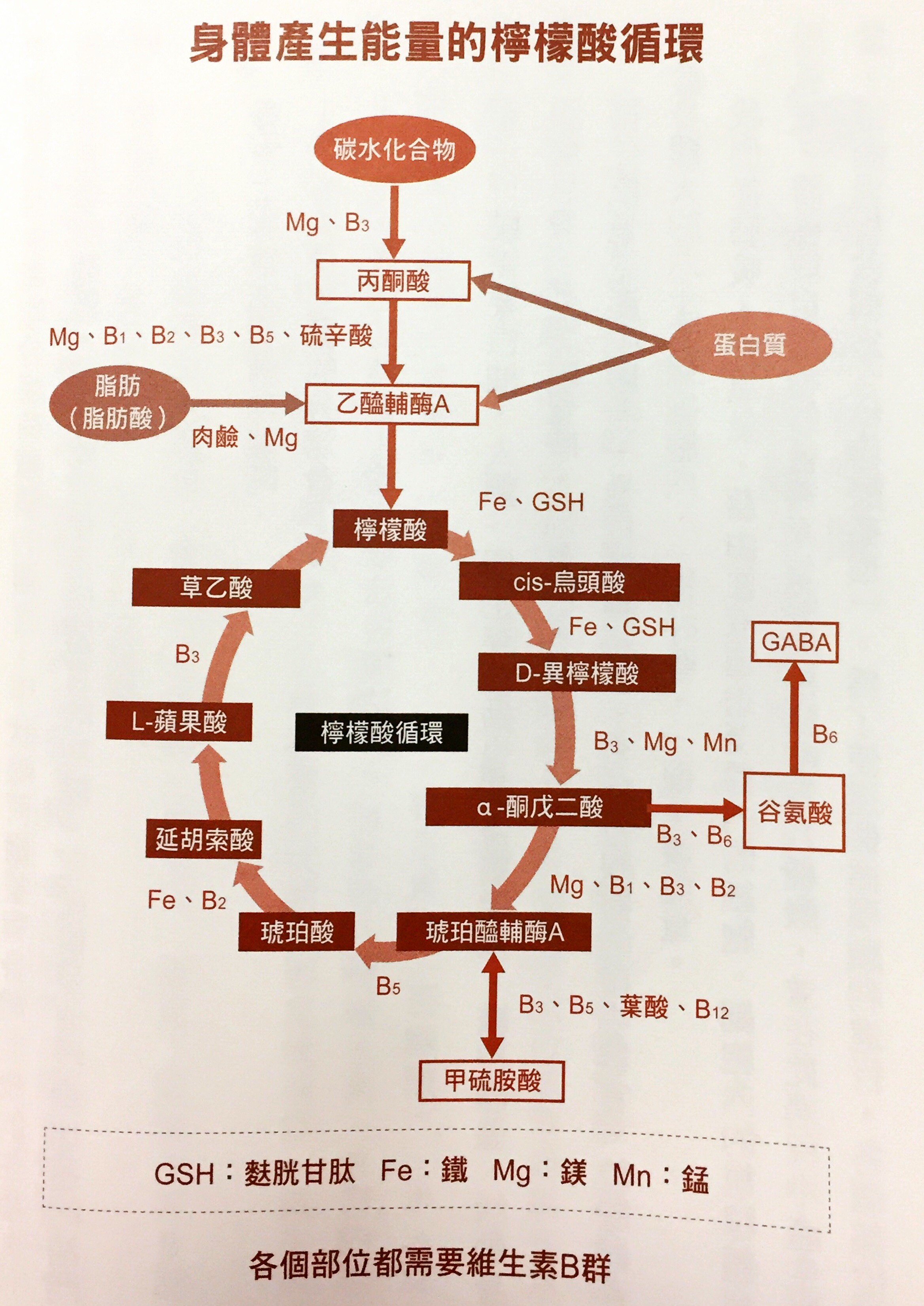
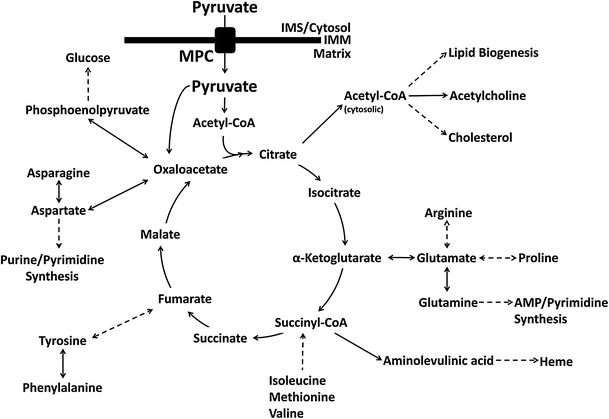
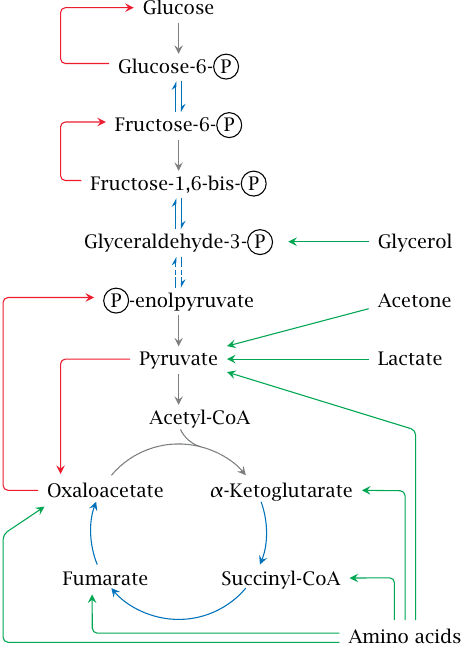
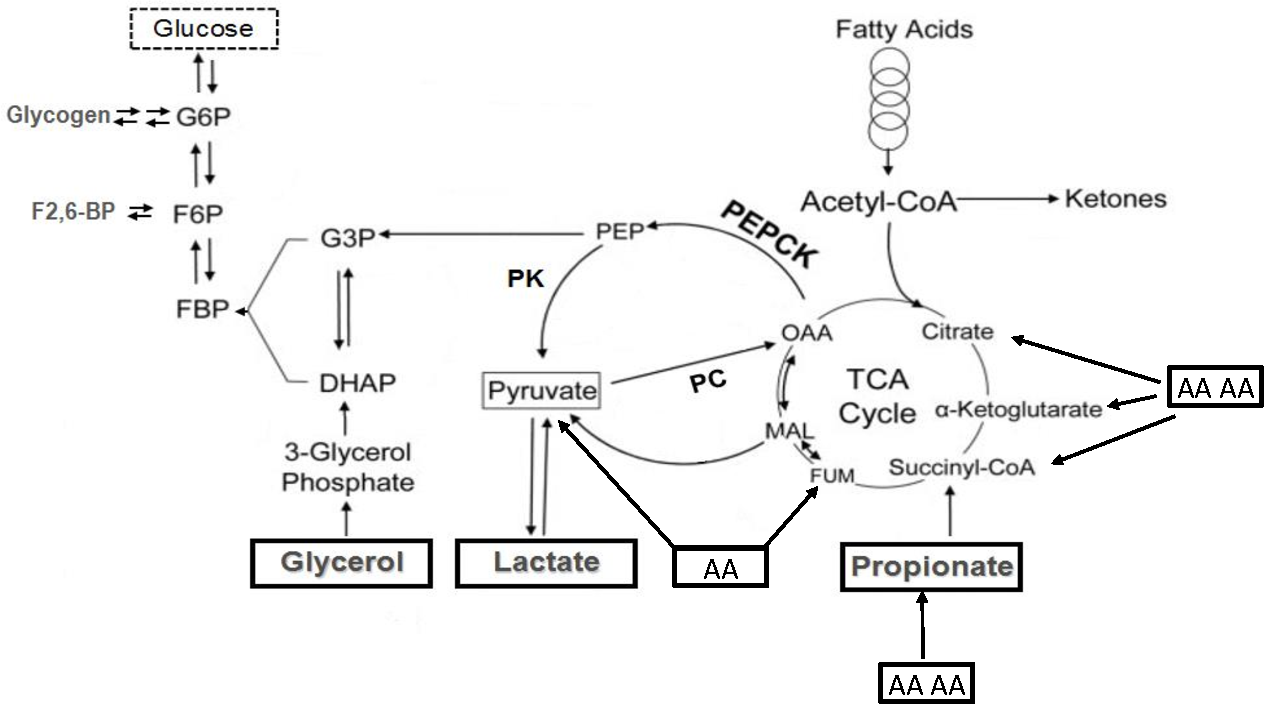
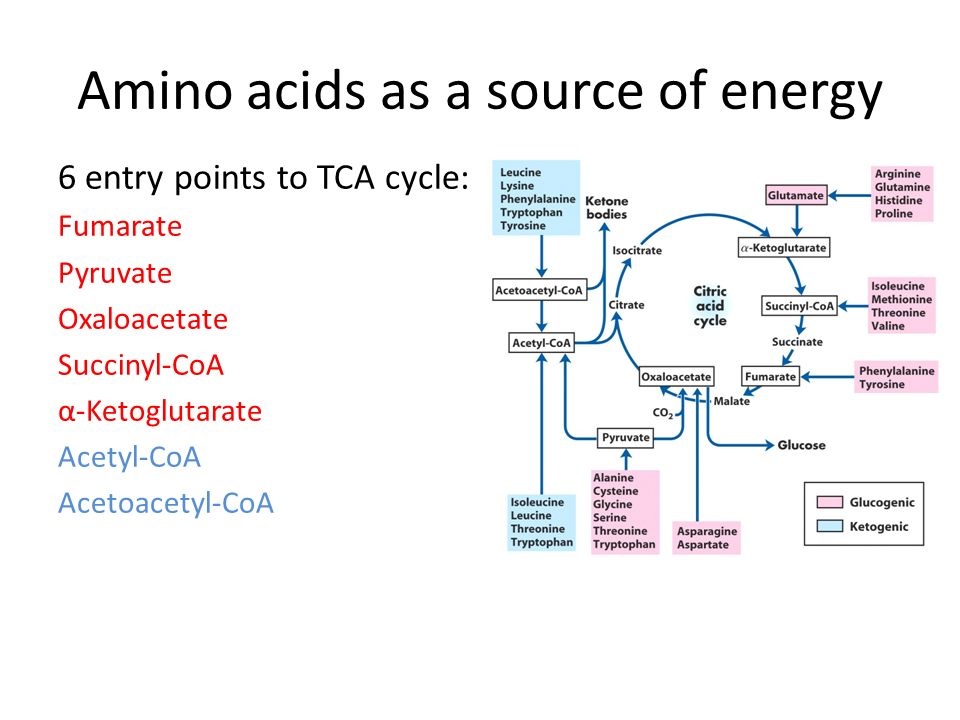
It is
not only used as a healthy lifestyle, it is also used for conditions
such as infantile spasms, epilepsy, autism, brain tumors, Alzheimer’s
disease, Lou Gehrig’s disease, depression, stroke, head trauma,
Parkinson’s disease, migraine, sleep disorders, schizophrenia, anxiety,
ADHD, irritability, polycystic ovarian disease, irritable bowel
syndrome, gastroesophageal reflux, obesity, cardiovascular disease,
acne, type 2 diabetes, tremors, respiratory failure and virtually every
neurological problem but also cancer, and conditions were tissues need
to recover after a loss of oxygen.[4]
Our body
organs and tissues work much better when they use ketones as a source of
fuel, including the brain, heart and the core of our kidneys. If you
ever had a chance to see a heart working in real time, you might have
noticed the thick fatty tissue that surrounds it. In fact, heart
surgeons get to see this every day. A happy beating heart is one that is
surrounded by layers of healthy fat. Both the heart and the brain run at
least 25% more efficiently on ketones than on blood sugar.
Ketones
are the ideal fuel for our bodies unlike glucose – which is damaging,
less stable, more excitatory and in fact shortens your life span.
Ketones are non-glycating, which is to say, they don’t have a
caramelizing aging effect on your body. A healthy ketosis also helps
starve cancer cells as they are unable to use ketones for fuel, relying
on glucose alone for their growth. [5]The
energy producing factories of our cells – the mitochondria – work much
better on a ketogenic diet as they are able to increase energy levels on
a stable, long-burning, efficient, and steady way. Not only that, a
ketogenic diet induces epigenetic changes[6] which increases the
energetic output of our mitochondria, reduces the production of damaging
free radicals, and favors the production of GABA – a major inhibitory
brain chemical. GABA has an essential relaxing influence and its favored
production by ketosis also reduces the toxic effects of excitatory
pathways in our brains. Furthermore, recent data suggests that ketosis
alleviates pain other than having an overall anti-inflammatory effect.
[7]
The
ketogenic diet acts on multiple levels at once, something that no drug
has been able to mimic. This is because mitochondria is specifically
designed to use fat for energy. When our mitochondria uses fat as an
energetic source, its toxic load is decreased, expression of energy
producing genes are increased, its energetic output is increased, and
the load of inflammatory energetic-end-products is decreased.
The key
of these miraculous healing effects relies in the fact that fat
metabolism and its generation of ketone bodies (beta-hydroxybutyrate and
acetoacetate) by the liver can only occur within the mitochondrion,
leaving chemicals within the cell but outside the mitochondria readily
available to stimulate powerful anti-inflammatory antioxidants. The
status of our mitochondria is the ultimate key for optimal health and
while it is true that some of us might need extra support in the form of
nutritional supplementation to heal these much needed energy factories,
the diet still remains the ultimate key for a proper balance.
Our
modern world’s staple energetic source is sugar which needs to be
processed first in the cell soup before it can be passed into the energy
factory of the cell- the mitochondrion. Energy sources from fat don’t
require this processing; it goes directly into the mitochondria for
energetic uses. That is, it is more complicated to create energy out of
sugar than out of fat. As Christian B. Allan, PhD and Wolfgang Lutz, MD
said in their book Life Without Bread:
Carbohydrates are not required to obtain energy. Fat supplies more
energy than a comparable amount of carbohydrate, and low-carbohydrate
diets tend to make your system of producing energy more efficient.
Furthermore, many organs prefer fat for energy.
The fact
is you get MORE energy per molecule of fat than sugar. How many chronic
and autoimmune diseases have an energy deficit component? How about
chronic fatigue? Fibromyalgia? Rheumatoid Arthritis? Multiple
Sclerosis? Cancer? Back to Allan and Lutz:
Mitochondria are the power plants of the cell. Because they produce most
of the energy in the body, the amount of energy available is based on
how well the mitochondria are working. Whenever you think of energy,
think of all those mitochondria churning out ATP to make the entire body
function correctly. The amount of mitochondria in each cell varies, but
up to 50 percent of the total cell volume can be mitochondria. When you
get tired, don’t just assume you need more carbohydrates; instead, think
in terms of how you can maximize your mitochondrial energy production…
If you
could shrink to a small enough size to get inside the mitochondria, what
would you discover? The first thing you’d learn is that the mitochondria
are primarily designed to use fat for energy!
In
short, let fat be thy medicine and medicine be thy fat!
You will
think that with all of this information we would see ketogenic diets
recommended right and left by our health care providers, but alas, that
is not the case. Mainstream nutritionists recommend carbohydrates AKA
sugar as the main staple of our diets. The problem with this (and there
are several of them) is that in the presence of a high carb diet we are
unable to produce ketones from the metabolism of fats, thus, depriving
ours bodies from much healing ketone production. The fact that we live
in a world which uses glucose as a primary fuel means that we eat a very
non healing food in more ways than one.
We
have been on a ketogenic diet for nearly three million years and it has
made us human. It was the lifestyle in which our brains got nurtured and
evolved. But not anymore, unless we all make an effort to reclaim this
lost wisdom. Nowadays the human brain is not only shrinking, but brain
atrophy is the norm as we age and get plagued with diseases such as
Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, senile dementia and so forth.
In the
mean time new research is starting to elucidate the key role of our
mitochondria in the regulation of the cell cycle – the vital process by
which a single celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as
well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal
organs are renewed. In the complicated and highly choreographed events
surrounding cell-cycle progression, mitochondria are not simple
bystanders merely producing energy but instead are full-fledged
participants.[8] Given the significant amount of energy needed to make
all the nutrients required for cell division, it makes sense that some
coordination existed. This long ignored and overlooked connection
between the mitochondria and the cell cycle is something that is worthy
of considerable more attention as we understand the role of diet in our
bodies. We’ll have to take a closer look to this subject of ketosis, as
it really holds the key to unlock our transformational pathways that
will lead us to an outstanding healthy living.
Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Mitochondria are best known as the powerhouses of our cells since they
produce the cell’s energy. But they also lead the genetic orchestra
which regulates how every cell ages, divides, and dies. They help
dictate which genes are switched on or off in every single cell of our
organism. They also provide the fuel needed to make new brain
connections, repair and regenerate our bodies.
Whether
we are housewives, sportsmen or labor people, energy is a topic that
concerns us all, every day and in every way. Our well being, behavior
and ability to perform the tasks in front of us to do is our individual
measure of energy. But how we derive energy from the foods that we eat?
There
are many man-made myths surrounding energy production in the body and
which foods supply energy. Mainstream science says that carbohydrates
are what mitochondria use as fuel for energy production. This process is
called oxidative metabolism because oxygen is consumed in the process.
The energy produced by mitochondria is stored in a chemical “battery”, a
unique molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Energy-packed ATP
can then be transported throughout the cell, releasing energy on demand
of specific enzymes. In addition to the fuel they produce, mitochondria
also create a by-product related to oxygen called reactive oxygen
species (ROS), commonly known as free radicals. But what we are not told
is that mitochondria were specifically designed to use fat for energy,
not carbohydrate.
|
Source: Christian B.
Allan, PhD and Wolfgang Lutz, MD, Life Without Bread. |
There
are several very complicated steps in making ATP within mitochondria,
but a look at 5 major parts of ATP production will be all that you need
to know in order to understand how energy is created within our
mitochondria and why fats are the key to optimize their function. Don’t
get focused on specific names, just try to see the whole picture.
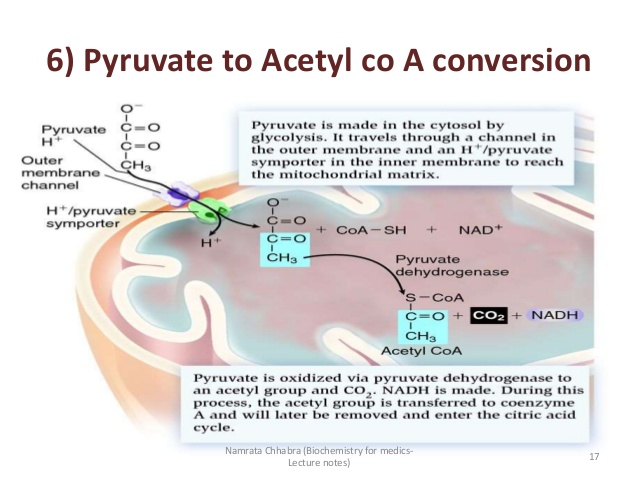
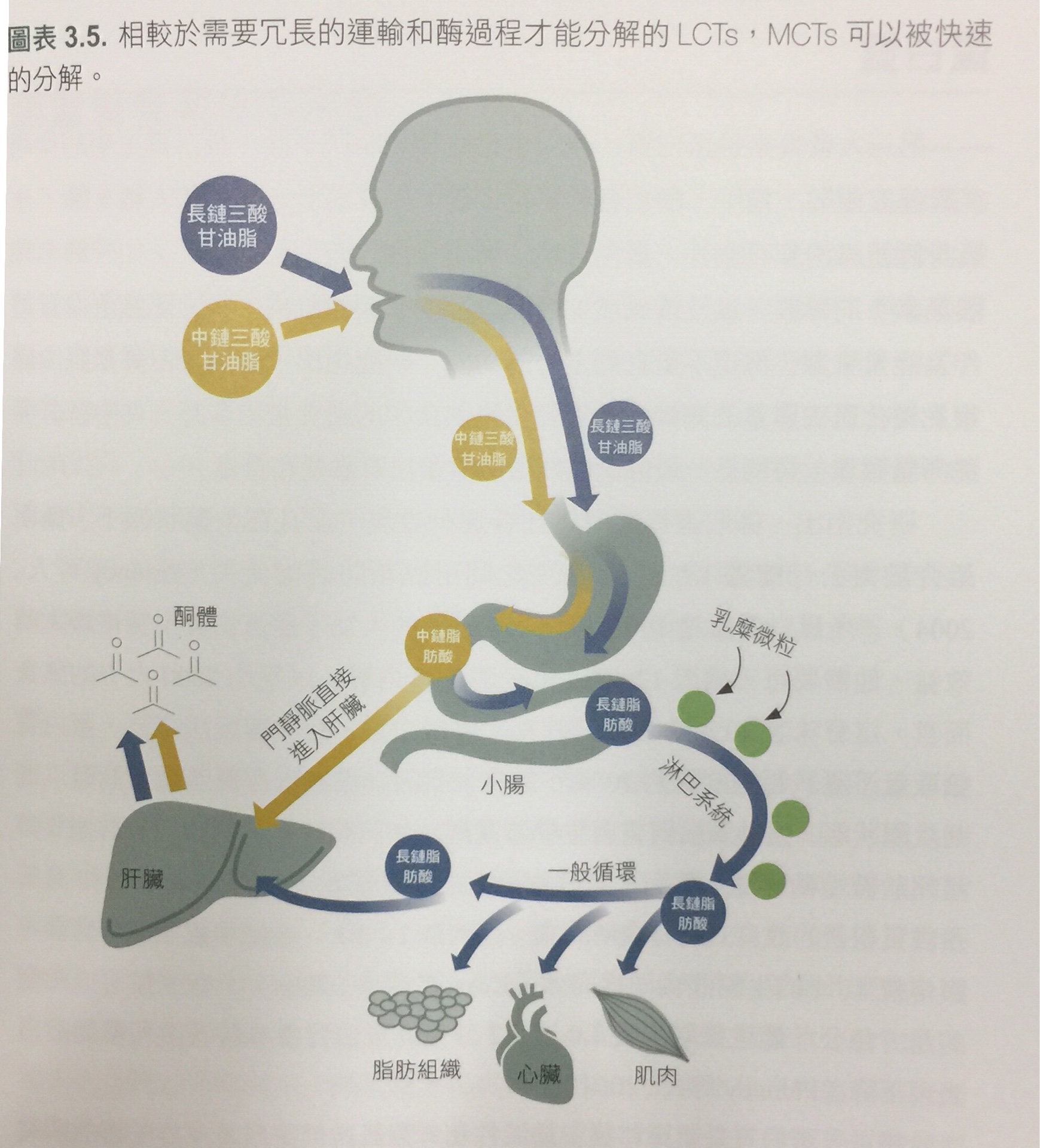
Step 1 – Transportation of Food-Based Fuel Source into the Mitochondria
Fuel
must first get into the mitochondria where all the action happens. Fuel
can come from carbs or it can come from fats. Fatty acids are the
chemical name for fat, and medium and large sized fatty acids get into
the mitochondria completely intact with the help of L-carnitine. Think
of L-carnitine as a subway train that transports fatty acids into the
mitochondria. L-carnitine (from the Greek word carnis means meat or
flesh) is chiefly found in animal products.
Fuel
coming from carbs needs to get broken down first outside the
mitochondria and the product of this breakdown (pyruvate) is the one who
gets transported inside the mitochondria, or it can be used to produce
energy in a very inefficient way outside the mitochondria through
anaerobic metabolism which produces ATP when oxygen is not present.
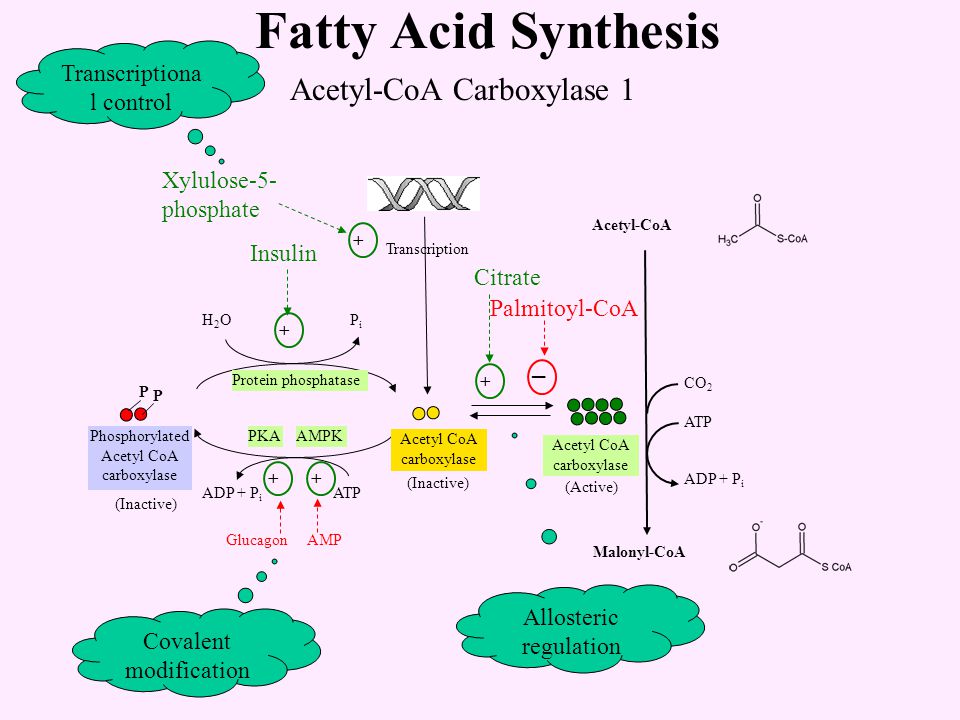
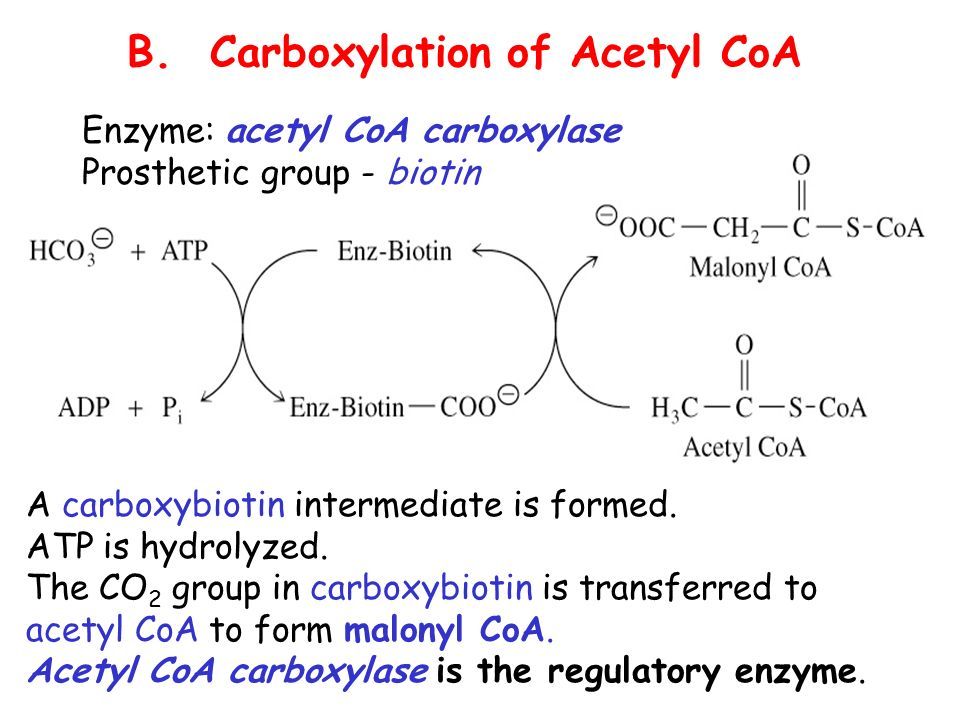
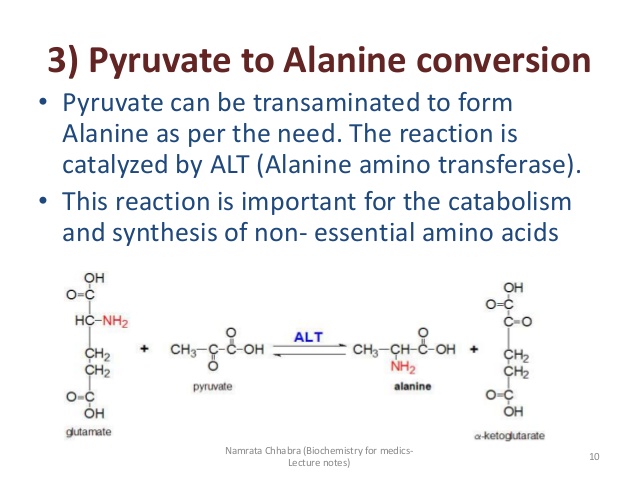
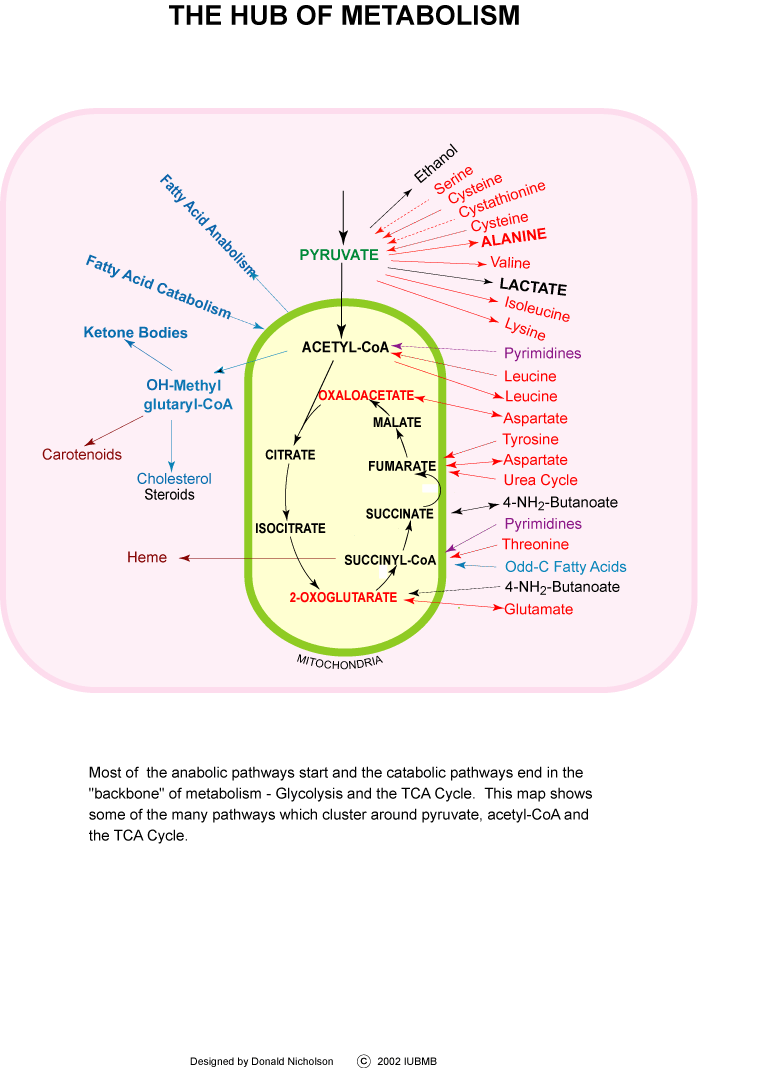
Step 2 – Fuel is Converted into Acetyl-CoA
When
pyruvate – the product of breaking down carbs – enters the mitochondria,
it first must be converted into acetyl-CoA by an enzymatic reaction.
Fatty
acids that are already inside the mitochondria are broken down directly
into acetyl-CoA in what is called beta-oxidation.
Acetyl-CoA
is the starting point of the next step in the production of ATP inside
the mitochondria.
Step 3 – Oxidation of Acetyl-CoA and the Krebs Cycle
The
Krebs cycle (AKA tricarboxylic acid cycle or citric acid cycle) is the
one that oxidizes the acetyl-CoA, removing thus electrons from acetyl-CoA
and producing carbon dioxide as a by-product in the presence of oxygen
inside the mitochondria.
Step 4 – Electrons Are Transported Through the Respiratory Chain
The
electrons obtained from acetyl-CoA – which ultimately came from carbs or
fats – are shuttled through many molecules as part of the electron
transport chain inside the mitochondria. Some molecules are proteins,
others are cofactors molecules. One of these cofactors is an important
substance found mainly in animal foods and it is called coenzyme Q-10.
Without it, mitochondrial energy production would be minimal. This is
the same coenzyme Q10 that statins drug block producing crippling
effects on people’s health. Step 4 is also where water is produced when
oxygen accepts the electrons.
Step 5 – Oxidative phosphorylation
As
electrons travel down the electron transport chain, they cause
electrical fluctuations (or chemical gradients) between the inner and
outer membrane in the mitochondria. These chemical gradients are the
driving forces that produce ATP in what is called oxidative
phosphorylation. Then the ATP is transported outside the mitochondria
for the cell to use as energy for any of its thousands of biochemical
reactions.
But why is fat better than carbs?
If there
were no mitochondria, then fat metabolism for energy would be limited
and not very efficient. But nature provided us during our evolution with
mitochondria that specifically uses fat for energy. Fat is the fueled
that animals use to travel great distances, hunt, work, and play since
fat gives more packed-energy ATPs than carbs. Biochemically, it makes
sense that if we are higher mammals who have mitochondria, then we need
to eat fat. Whereas carb metabolism yields 36 ATP molecules from a
glucose molecule, a fat metabolism yields 48 ATP molecules from a fatty
acid molecule inside the mitochondria. Fat supplies more energy for the
same amount of food compared to carbs. But not only that, the burning of
fat by the mitochondria – beta oxidation – produces ketone bodies that
stabilizes overexcitation and oxidative stress in the brain related to
all its diseases, it also causes epigenetic changes that produce healthy
and energetic mitochondria and decreasing the overproduction of damaging
and inflammatory free radicals among many other things!
Mitochondria regulate cellular suicide, AKA apoptosis, so that old and
dysfunctional cells which need to die will do so, leaving space for new
ones to come into the scene. But when mitochondria function becomes
impaired and send signals that tell normal cells to die, things go
wrong. For instance, the destruction of brain cells leads to every
single neurodegenerative condition known including Alzheimer’s disease,
Parkinson’s disease and so forth. Mitochondrial dysfunction has
wide-ranging implications, as the health of the mitochondria intimately
affects every single cell, tissue and organ within your body.
The
catalysts for this destruction is usually uncontrolled free radical
production which cause oxidative damage to tissues, fat, proteins, DNA;
causing them to rust. This damage, called oxidative stress, is at the
basis of oxidized cholesterol, stiff arteries (rusty pipes) and brain
damage. Oxidative stress is a key player in dementia as well as autism.
We
produce our own anti-oxidants to keep a check on free radical
production, but these systems are easily overwhelmed by a toxic
environment and a high carb diet, in other words, by today’s lifestyle
and diet.
Mitochondria also have interesting characteristics which differentiate
them from all other structural parts of our cells. For instance, they
have their own DNA (referred as mtDNA) which is separate from the widely
known DNA in the nucleus (referred as n-DNA),. Mitochondrial DNA comes
for the most part from the mother line, which is why mitochondria is
also considered as your feminine life force. This mtDNA is arranged in a
ring configuration and it lacks a protective protein surrounding,
leaving its genetic code vulnerable to free radical damage. If you don’t
eat enough animal fats, you can’t build a functional mitochondrial
membrane which will keep it healthy and prevent them from dying.
If you
have any kind of inflammation from anywhere in your body, you damage
your mitochondria. The loss of function or death of mitochondria is
present in pretty much every disease. Dietary and environmental factors
lead to oxidative stress and thus to mitochondrial injury as the final
common pathway of diseases or illnesses.
Autism,
ADHD, Parkinson’s, depression, anxiety, bipolar disease, brain aging are
all linked with mitochondrial dysfunction from oxidative stress.
Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to congestive heart failure, type
2 diabetes, autoimmune disorders, aging, cancer, and other diseases.
Whereas
the nDNA provides the information your cells need to code for proteins
that control metabolism, repair, and structural integrity of your body,
it is the mtDNA which directs the production and utilization of your
life energy. A cell can still commit suicide (apoptosis) even when it
has no nucleus nor nDNA.
Because
of their energetic role, the cells of tissues and organs which require
more energy to function are richer in mitochondrial numbers. Cells in
our brains, muscles, heart, kidney and liver contain thousands of
mitochondria, comprising up to 40% of the cell’s mass. According to
Prof. Enzo Nisoli, a human adult possesses more than ten million billion
mitochondria, making up a full 10% of the total body weight.[9] Each
cell contains hundreds of mitochondria and thousands of mtDNA.
Since
mtDNA is less protected than nDNA because it has no “protein” coating (histones),
it is exquisitely vulnerable to injury by destabilizing molecules such
as neurotoxic pesticides, herbicides, excitotoxins, heavy metals and
volatile chemicals among others. This tips off the balance of free
radical production to the extreme which then leads to oxidative stress
damaging our mitochondria and its DNA. As a result we get overexcitation
of cells and inflammation which is at the root of Parkinson’s disease
and other diseases, but also mood problems and behavior problems.
Enough
energy means a happy and healthy life. It also reflects in our brains
with focused and sharp thinking. Lack of energy means mood problems,
dementia, and slowed mental function among others. Mitochondria are
intricately linked to the ability of the prefrontal cortex –our brain’s
captain- to come fully online. Brain cells are loaded in mitochondria
that produce the necessary energy to learn and memorize, and fire
neurons harmoniously.
The
sirtuin family of genes works by protecting and improving the health and
function of your mitochondria.[10] They are positively influenced by a
diet that is non-glycating, i.e. a low carb diet as opposed to a high
carb diet which induces mitochondrial dysfunction and formation of
reactive oxygen species.
Another thing that contributes to mitochondrial dysfunction is latent
viral infection such as the ones of the herpes family. As I mentioned in On
Viral “Junk” DNA, a DNA Enhancing Ketogenic Diet, and Cometary Kicks,
most, if not all of your “junk” DNA has viral-like properties. If a
pathogenic virus takes hold of our DNA or RNA, it could lead to disease
or cancer.
Herpes
simplex virus is a widespread human pathogen and it goes right after our
mitochondrial DNA. Herpes simplex virus establishes its latency in
sensory neurons, a type of cell that is highly sensitive to the
pathological effects of mt DNA damage.[11] A latent viral infection
might be driving the brain cell loss in neurodegenerative diseases such
as Alzheimer’s disease.[12]As I speculated in Heart
attacks, CFS, herpes virus infection and the vagus nerve ,
a latent herpes virus infection might drive more diseases than we would
like to admit.
Members
of the herpes virus family (i.e. cytomegalovirus and Epstein-Barr virus
which most people have as latent infections!), can go after our
mitochondrial DNA, causing neurodegenerative diseases by mitochondrial
dysfunction. But a ketogenic diet is the one thing that would help
stabilize mtDNA since mitochondria runs the best on fat fuel. As it
happens, Alzheimer’s disease is the one condition where a ketogenic diet
has its most potential healing effect.[4]
The role
of mitochondrial dysfunction in our “modern” age maladies is a
staggering one. Optimal energetic sources are essential if we are to
heal from chronic ailments. It is our mitochondria which lies at the
interface between the fuel from foods that come from our environment and
our bodies’ energy demands. And it is a metabolism based on fat fuel, a
ketone metabolism, the one which signals epigenetic changes that
maximizes energetic output within our mitochondria and help us heal.
|
I am incredulous at
how my body is responding. I think I am totally carb
intolerant. I’ve struggled with extreme fatigue/exhaustion for
so many years, even with improved sleep in a dark room that I
can’t tell you how wonderful it is to wake up in the morning,
get out of bed and not long to crawl back in, going through the
day by will mostly. Also chronic long-standing intestinal
issues are finally resolving. A couple of people at work have
made comments to the effect that I’m a “different woman”,
calmer, no more hyperness under pressure, stress seems to roll
off of my back as well. I’ve lost a little weight and although
I don’t weigh myself, my clothes are definitely looser. I’ve
had the round middle for so many years I was resigned to
struggling to bend over to pull my shoes on! -Bluefyre, 56
years old, United States. Sott.net forum |
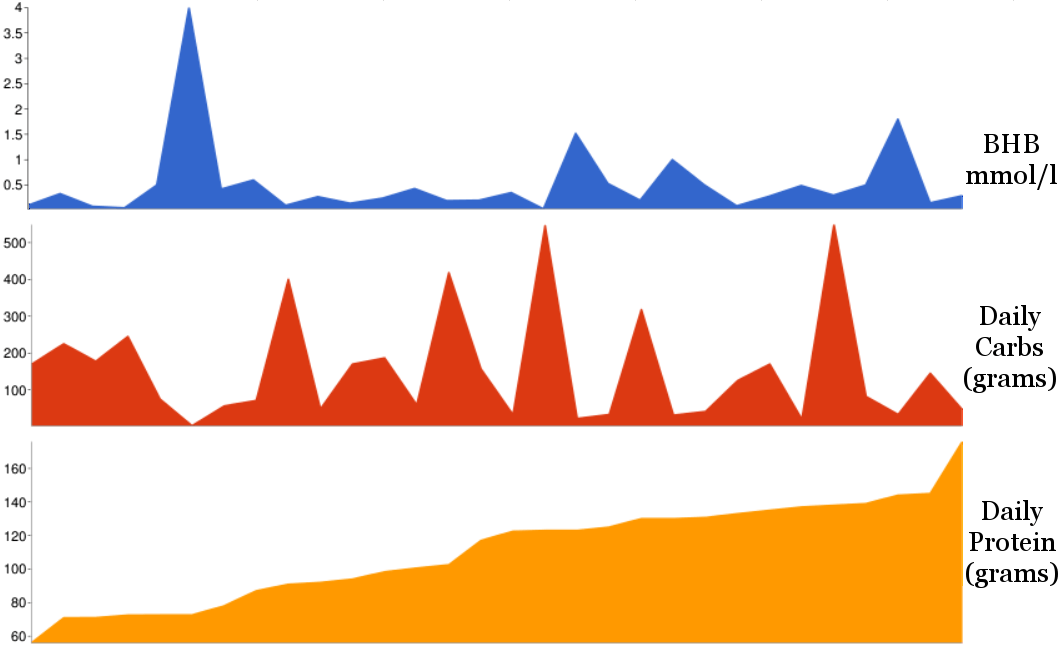
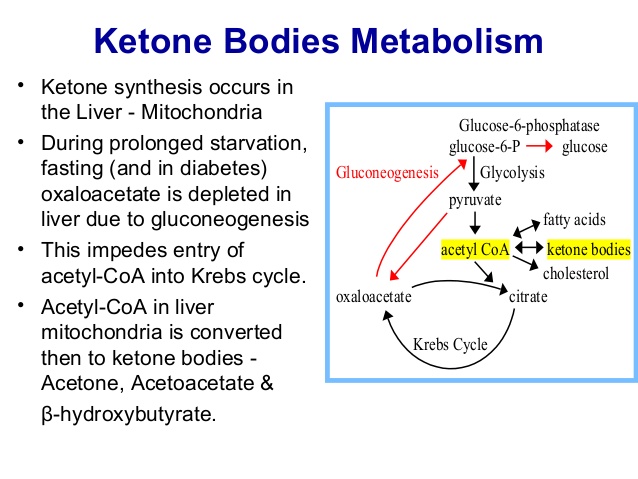
Ketosis – Closer Look
The
presence of ketones in the blood and urine, a condition known as
ketosis, has always been regarded as a negative situation, related to
starvation. While it is true that ketones are produced during fasting,
ketones are also produced in times of plenty, but not plenty of
carbohydrates since a carb metabolism suppresses ketosis. In the absence
of most carbs in the diet, ketones will form from fat to supply for
energy. This is true even if lots of fats and enough protein are eaten,
something that is hardly a starvation condition.
As we
already saw, a ketogenic diet has been proved useful in a number of
diseases, especially neurological ones. Strictly speaking, a ketogenic
diet is a high fat diet in which carbohydrates are either completely
eliminated or nearly eliminated so that the body has the very bare
minimum sources of glucose. That makes fats (fatty acids) a mandatory
energetic fuel source for both the brain and other organs and tissues.
If you are carb intake is high, you’ll end up storing both the fat and
the carbs in your fat tissue thanks to the hormone insulin. A ketogenic
diet is not a high protein diet, which as it happens, can also stimulate
insulin. It is basically a diet where you rely primarily on animal foods
and especially their fats.
|
I recently had my
annual blood work done (cholesterol, etc.) During the review, my
doctor said that everything looked great! He then encouraged me
to continue on my great ‘low fat, high fruit and veggie diet’
that I must be following! I just smiled. Next visit I’m going to
tell him about my real ‘diet’. Lol -1984, United States.
Sott.net forum. |
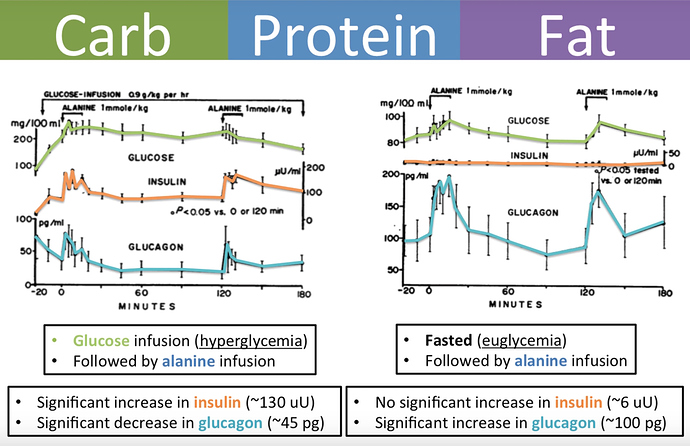
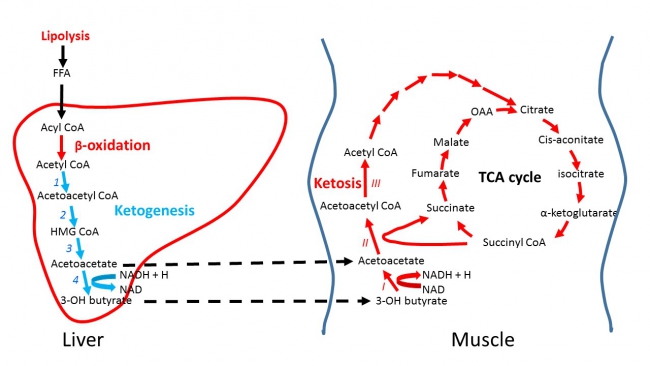
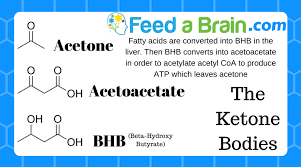
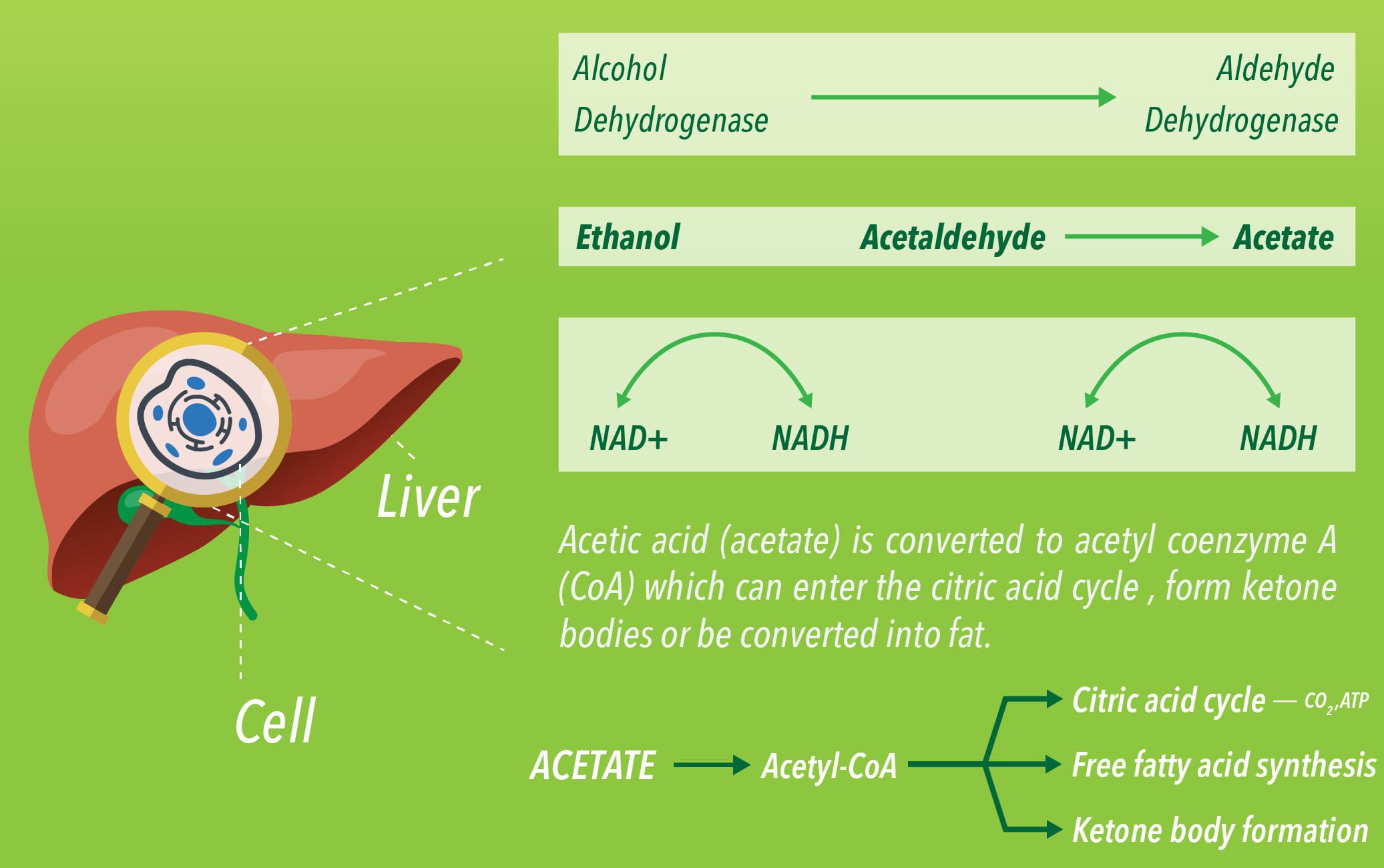
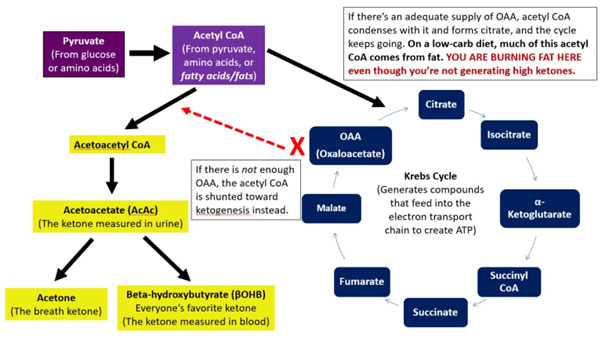
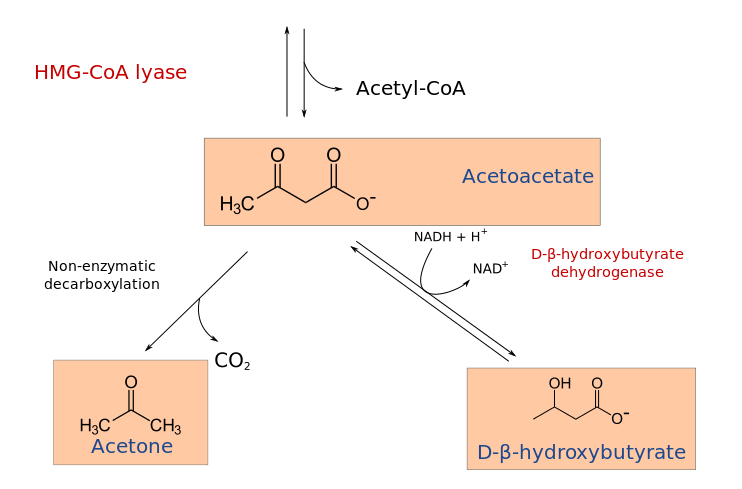
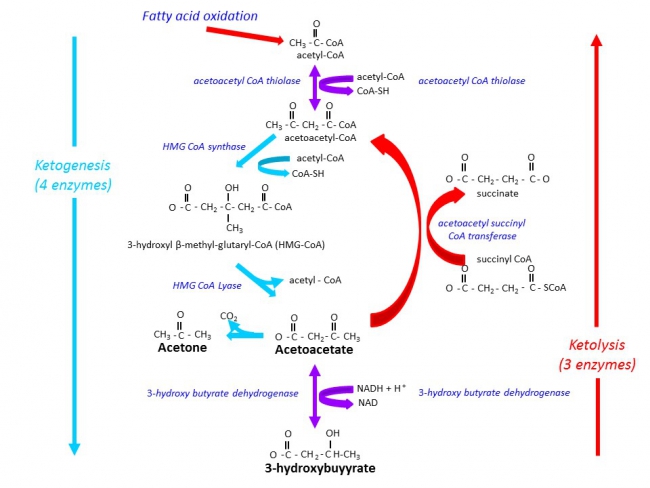
Among
the by-products of fat burning metabolism are the so called ketone
bodies – acetoacetate, β-hydroxybutyrate and acetone – which are
produced for the most part by the liver. When our bodies are running
primarily on fats, large amounts of acetyl-CoA are produced which exceed
the capacity of the Krebs cycle, leading to the making of these three
ketone bodies within liver mitochondria. Our levels of ketone bodies in
our blood go up and the brain readily uses them for energetic purposes.
Ketone bodies cross the blood brain barrier very readily. Their
solubility also makes them easily transportable by the blood to other
organs and tissues. When ketone bodies are used as energy, they release
acetyl-CoA which then goes to the Krebs cycle again to produce energy.
In
children who were treated with the ketogenic diet to treat their
epilepsy, it was seen that they become seizure-free even long after the
diet ended, meaning that not only did the diet proved to be protective,
but also it modified the activity of the disease , something that no
drug has been able to do.[13] In Alzheimer’s disease, as levels of
ketone bodies rise, memory improves. People’s starved brains finally
receive the much needed fats they need! In fact, every single
neurological disease is improved on the ketogenic diet.
The
benefits of a ketogenic diet can be seen as fast as one week, developing
gradually over a period of 3 weeks. There are several changes in gene
expression involving metabolism, growth, development, and homeostasis
among others.
The
hippocampus is a region in your brain that is very vulnerable to stress
which makes it lose its brain cells. The hippocampus has to do with
memory, learning, and emotion. As it happens, a ketogenic diet promotes
the codification of genes which creates mitochondria in the hippocampus,
making more energy available. A larger mitochondrial load and more
energy means more reserve to withstand much more stress.[14]
In some
animal models, there is a 50% increase in the total number of
mitochondria in the hippocampus, resulting in more brain ATP.[15] Other
animal studies show how communication between brain cells in the
hippocampus would remain smooth for 60% longer when exposed to a
stressful stimulus compared to their counterparts who didn’t had a
ketogenic diet.[16] This is very important since too much stress can
damage the hippocampus and its capacity to retrieve information, making
you “absent-minded” or “brain-scattered”, as well as affecting the
ability of your prefrontal cortex to think and manage behavior.
A
ketogenic diet also increases levels of the calming neurotransmitter –
GABA which then serves to calm down the overexcitation which is at the
base of major neurodegenerative diseases, but also anxiety and other
mood problems. A ketogenic diet also increases antioxidant pathways that
level the excess production of free radicals from a toxic environment.
It also enhances anti-inflammatory pathways.
Ketosis also cleans our cells from proteins that act like “debris” and
which contribute to aging by disrupting a proper functioning of the
cell.[17] It basically does this by what is known as autophagy which
preserves the health of cells and tissues by replacing outdated and
damaged cellular components with fresh ones. This prevents degenerative
diseases, aging, cancer, and protects you against microbial infections.A
ketogenic diet not only rejuvenates you, it also makes a person much
less susceptible to viruses and bacterial infections.[18] This is very
relevant due to the increasing number of weird viral and bacterial
infections that seem to be incoming from our upper atmosphere[19] (for
more information see New
Light on the Black Death: The Viral and Cosmic Connection),
or due to high levels of radiation that creates more pathogenic strains
(see Detoxify
or Die: Natural Radiation Protection Therapies for Coping With the
Fallout of the Fukushima Nuclear Meltdown). Either or, we are
more vulnerable than ever due to the state of our mitochondria. But we
can prepare for the worst with ketosis.
Ketone-enhanced
autophagy is very important because autophagy can target viruses and
bacteria that grow inside cells which are very problematical.[20]
Intracellular viruses and bacteria can lead to severe mitochondrial
dysfunction and ketosis remains by far our best chance against them.
Ketone
bodies production through intermittent fasting and the ketogenic diet is
the most promising treatment for mitochondrial dysfunction.[21]The
longevity benefits seen caloric restriction research is due to the fact
that our bodies shift to a fat burning metabolism within our
mitochondria. With a ketogenic diet, we go into a fat burning metabolism
without restricting our caloric intake.
Ketosis
deals effectively with all the problems of a diet rich in carbs – the
one recommended by mainstream science: anxiety, food cravings,
irritability, tremors, and mood problems among others. It is a crime to
discourage the consumption of a high fat diet considering that a
ketogenic diet shrinks tumors on human and animal models, and enhances
our brain’s resiliency against stress and toxicity.
In
addition to increasing the production of our body’s natural valium –
GABA – the increased production of acetyl-CoA generated from the ketone
bodies also drives the Krebs cycle to increase mitochondrial NADH
(reduced nicotinamide adenine nucleotide) which our body uses in over
450 vital biochemical reactions – including the cell signaling and
assisting of the ongoing DNA repair. Because the ketone body beta-hydroxybutyrate
is more energy rich than pyruvate, it produces more ATP. Ketosis also
enhances the production of important anti-oxidants that deal with toxic
elements from our environments, including glutathione.
Mitochondria from the hippocampus of ketogenic diet-fed animals are also
resistant to mtDNA damage and are much less likely to commit cell
suicide –apoptosis- at inappropriate times.
As
Douglas C. Wallace, PhD, Director of the Center for Mitochondrial and
Epigenomic Medicine says, “the ketogenic diet may act at multiple
levels: It may decrease excitatory neuronal activity, increase the
expression of bioenergetic genes, increase mitochondrial biogenesis and
oxidative energy production, and increase mitochondrial NADPH
production, thus decreasing mitochondrial oxidative stress.”[21]
Keto-adaptation
results in marked changes in how we construct and maintain optimum
membrane (“mem-brain”) composition, not only because of the healthy fats
we provide through the diet, but also because of less free radical
production and inflammatory mediators, along with more production of
anti-oxidants. It is really the ideal balanced state.
Moreover, you might want to keep in mind this excerpt from Human Brain
Evolution: The Influence of Freshwater and Marine Food Resources[22]:
“There
are two key advantages to having ketone bodies as the main alternative
fuel to glucose for the human brain. First, humans normally have
significant body fat stores, so there is an abundant supply of fatty
acids to make ketones. Second, using ketones to meet part of the brain’s
energy requirement when food availability is intermittent frees up some
glucose for other uses and greatly reduces both the risk of detrimental
muscle breakdown during glucose synthesis, as well as compromised
function of other cells dependent on glucose, that is, red blood cells.
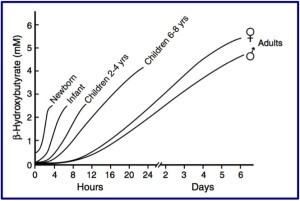
One interesting attribute of ketone uptake by the brain is that it is
four to five times faster in newborns and infants than in adults. Hence,
in a sense, the efficient use of ketones by the infant brain means that
it arguably has a better fuel reserve than the adult brain. Although the
role of ketones as a fuel reserve is important, in infants, they are
more than just a reserve brain fuel – they are also the main substrate
for brain lipid synthesis.
I have
hypothesized that evolution of a greater capacity to make ketones
coevolved with human brain expansion. This increasing capacity was
directly linked to evolving fatty acid reserves in body fat stores
during fetal and neonatal development. To both expand brain size and
increase its sophistication so remarkably would have required a reliable
and copious energy supply for a very long period of time, probably at
least a million, if not two million, years. Initially, and up to a
point, the energy needs of a somewhat larger hominin brain could be met
by glucose and short – term glucose reserves such as glycogen and
glucose synthesis from amino acids. As hominins slowly began to evolve
larger brains after having acquired a more secure and abundant food
supply, further brain expansion would have depended on evolving
significant fat stores and having reliable and rapid access to the fuel
in those fat stores. Fat stores were necessary but were still not
sufficient without a coincident increase in the capacity for
ketogenesis. This unique combination of outstanding fuel store in body
fat as well as rapid and abundant availability of ketones as a brain
fuel that could seamlessly replace glucose was the key fuel reserve for
expanding the hominin brain, a reserve that was apparently not available
to other land – based mammals, including nonhuman primates.”
It is
indisputable that a ketogenic diet has protective effects in our brains.
With all the evidence of its efficacy in mitochondrial dysfunction, it
can be applied for all of us living in a highly stressful and toxic
environment. Ketone bodies are healing bodies that helped us evolve and
nowadays our mitochondria are always busted in some way or another since
the odds in this toxic world are against us. Obviously, there are going
to be people with such damaged mtDNA or with mutations they were born
with, who can’t modify their systems (i.e. defects on L-carnitine
metabolism), but even in some of those cases, they can halt or slow down
further damage. Our healthy ancestors never had to deal with the levels
of toxicity that we live nowadays and nevertheless, they ate optimally.
Considering our current time and environment, the least we can do is eat
optimally for our physiology.
The way
to have healing ketone bodies circulating in our blood stream is to do a
high fat, restricted carb and moderated protein diet. Coupled with
intermittent fasting which will enhance the production of ketone bodies,
and resistance training which will create mitochondria with healthier
mtDNA, we can beat the odds against us.
What is
considered nowadays a “normal diet” is actually an aberration based on
the corruption of science which benefits Big Agra and Big Pharma. If we
would go back in time to the days before the modern diet became
normalized by corporative and agricultural interests, we will find that
ketosis was the normal metabolic state. Today’s human metabolic state is
aberrant. It is time to change that.
References
[1] A
research member of sott.net’s forum has diabetes type 1 and is doing the
ketogenic diet. On normal circumstances, diabetics (including type I)
report amazing results on a low-carbohydrate diet. See Dr. Bernstein’s
Diabetics Solution by Richard K. Bernstein, MD (Little, Brown and
Company: 2007).
[2] It
varies among each person, but the general range is between 0 and 70
grams of carbs plus moderate intake of protein, between 0.8 and 1.5
grams of protein per kg of ideal body weight. Pregnant women and
children should not have their protein restricted.
[3]
Ketogenic diets in seizure control and neurologic disorders by Eric
Kossoff, MD, Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore, Maryland. The Art and
Science of Low Carbohydrate Living by Jeff S. Volek, PhD, Rd and Stephen
D. Phinney, MD, PhD. Beyond Obesity, LLC , 2011.
[4]A
Paoli, A Rubini, J S Volek and K A Grimaldi. Beyond weight loss: a
review of the therapeutic uses of very-low-carbohydrate (ketogenic)
diets. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2013) 67, 789–796
[5] Rainer
J Klement, Ulrike Kämmerer. Is there a role for carbohydrate restriction
in the treatment and prevention of cancer? Nutr Metab (Lond). Oct
26, 2011; 8: 75.
[6] If
the genetic code is the hardware for life, the epigenetic code is
software that determines how the hardware behaves.
[7]
David N. Ruskin and Susan A. Masino, The Nervous System and Metabolic
Dysregulation: Emerging Evidence Converges on Ketogenic Diet Therapy.
Front Neurosci. 2012; 6: 33.
[8]
Finkel T, Hwang PM. The Krebs cycle meets the cell cycle: mitochondria
and the G1-S transition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Jul
21;106(29):11825-6.
[9] Matthews
C.M. Nurturing your divine feminine. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2011
July; 24(3): 248.
[10]
Hipkiss AR. Energy metabolism, altered proteins, sirtuins and ageing:
converging mechanisms? Biogerontology.
2008 Feb;9(1):49-55.
[11] Saffran
HA, Pare JM, Corcoran JA, et al. Herpes
simplex virus eliminates host mitochondrial DNA. EMBO Rep. 2007
Feb;8(2):188-93.
[12] Porcellini
E, Carbone I, et al. Alzheimer’s
disease gene signature says: beware of brain viral infections. Immun
Ageing. 2010 Dec 14;7:16.
[13] Gasior
M, Rogawski MA, Hartman AL. Neuroprotective
and disease-modifying effects of the ketogenic diet. Behav Pharmacol.
2006 Sep;17(5-6):431-9.
[14]
Maalouf M, Rho JM, Mattson MP. The neuroprotective properties of calorie
restriction, the ketogenic diet, and ketone bodies. Brain Res Rev. 2009
Mar;59(2):293-315.
[15]
Nylen K, Velazquez JL. The effects of a ketogenic diet on ATP
concentrations and the number of hippocampal mitochondria in
Aldh5a1(-/-) mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Mar;1790(3):208-12.
[16]
Bough K. Energy metabolism as part of the anticonvulsant mechanism of
the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia. 2008 Nov;49 Suppl 8:91-3.
[17]
Finn PF, Dice JF. Ketone bodies stimulate chaperone-mediated autophagy.
J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 8;280(27):25864-70.
[18] Yuk
JM, Yoshimori T, Jo EK. Autophagy and bacterial infectious diseases. Exp
Mol Med. 2012 Feb 29;44(2):99-108.
[19]
Chandra Wickramasinghe, Milton Wainwright & Jayant Narlika. SARS – a
clue to its origins? The Lancet, vol. 361, May 23, 2003, pp 1832.
[20]
Yordy B, Iwasaki A. Autophagy in the control and pathogenesis of viral
infection. Curr Opin Virol. 2011 Sep;1(3):196-203.
[21]
Douglas C. Wallace, Weiwei Fan, and Vincent Procaccio. Mitochondrial
Energetics and Therapeutics Annu Rev Pathol. 2010; 5: 297–348.
[22]
Stephen Cunnane, Kathlyn Stewart.Human Brain Evolution: The Influence of
Freshwater and Marine Food Resources. June 2010, Wiley-Blackwell.


.jpg)